 |
|
 |
The Problems
- Electrostatic motor
Is it possible to create a motor
which works by means of an electrostatic field? If yes, suggest
how it may be constructed and estimate its parameters.
- Singing saw
Some people can play music on a
handsaw. How do they get different pitches? Give a quantitative
description of the phenomenon.
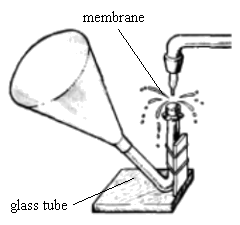
- Tuning dropper
Make the music resonator shown in the
picture. Investigate the conditions that affect the pitch. Can you
observe amplification of external sounds? If yes, how can you
explain this?
- Dancing sand clock
Investigate the trickling of sand
when a sand clock (egg-timer) is placed on a vibrating base.
- Rubber heat machine
Investigate the conversion of
energy in the process of deformation of rubber. Construct a heat
machine, which uses rubber as the working element and demonstrate
how it works.
- Fractal diffraction
Produce, demonstrate and analyse
diffraction pictures of fractal structures of different orders.
- Cracks
When drying a starch solution, you will see
cracks forming. Investigate and explain this phenomenon.
- Speedometer
Two electrodes of different metal are
immersed in an electrolyte solution. Investigate the dependence of
the measured potential difference on the relative motion of
electrodes and their shapes.
- Pouring out
Investigate how to empty a bottle filled
with a liquid as fast as possible, without external technical
devices.
- Water stream pump
Construct and demonstrate a water
stream vacuum pump. What is your record value for the minimum
pressure?
- Rolling balls
Place two equal balls in a horizontal,
V-shaped channel, with the walls at 90 degrees to each other, and
let the balls roll towards each other. Investigate and explain the
motion of the balls after the collision. Make experiments with
several different kinds of ball pairs and explain the results.
- Reaction
Make an aqueous solution of gelatine (10g
gelatine in 90ml of water), heat it to 80 degrees C in a water
bath and mix it with a solution of potassium iodide. Pour the
solution in a test tube and cool it. Pour a solution of copper
sulphate on the surface of the gel. Find a physical explanation to
the observed phenomena.
- Membrane electrolyser
In an electrolyser, containing a
membrane which completely divides the space between two inert
electrodes, the pH-value of the diluted salt solution will change
substantially after electrolysis. Investigate how this difference
depends on the pore size of the membrane.
- Thread dropper
One end of a thread is immersed in a
vessel filled with water. The other end hangs down outside without
contact with the outer wall of the vessel. Under certain
conditions, one can observe drops on that end of the thread. What
are those conditions? Determine how the time of appearance of the
first drop depends on relevant parameters.
- Bubbles in magnetic field
Observe the influence of an
alternating magnetic field (50 or 60 Hz) on the kinetics of gas
bubbles in a vessel filled with water. The bubbles can be
generated by blowing air into the water.
- Adhesive tape
Investigate and explain the light
produced, when adhesive tape is ripped from a smooth surface.
- Seiches
Seiching is a phenomenon shown by long and
narrow deep lakes. Due to changes in atmospheric pressure, the
water of the lake can start moving in such a way that its level at
both ends of the lake makes periodic motions, which are identical,
but out of phase. Make a model that predicts the period of
seiching (depending on appropriate parameters) and test its
validity.
Click
here to see a printer-friendly version of this
page. | |
 |
